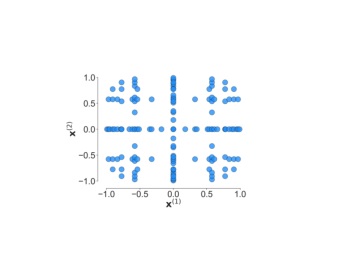
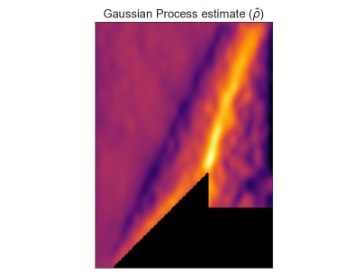
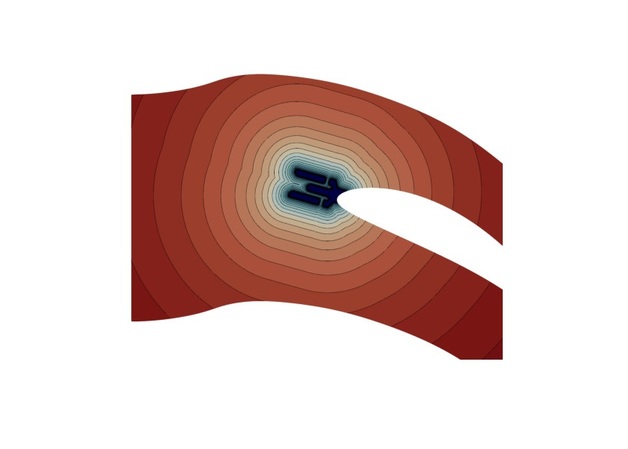
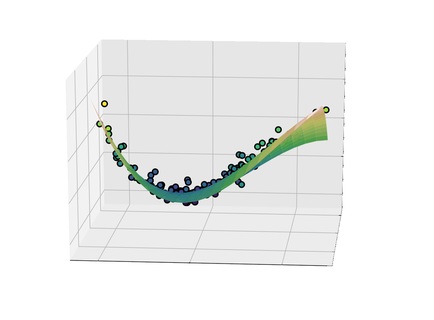
Blade envelopes Part II: Multiple objectives and inverse design
Journal: Journal of Turbomachinery
C. Y. Wong, P. Seshadri, A. Scillitoe, B. N. Ubald, A. Duncan, G. Parks
Blade envelopes offer a set of data-driven
tolerance guidelines for manufactured
components based on aerodynamic analysis. In
Part I of this two-part paper, a workflow for
the formulation of blade envelopes is
described and demonstrated. In Part II, this
workflow is extended to accommodate multiple
objectives. This allows engineers to prescribe
manufacturing guidelines that take into
account multiple performance criteria. The
quality of a manufactured blade can be
correlated with …
- Orthogonal Polynomials
- Dimension Reduction
- Sensitivity Analysis
- RANS
- 3D Modelling
- Blender